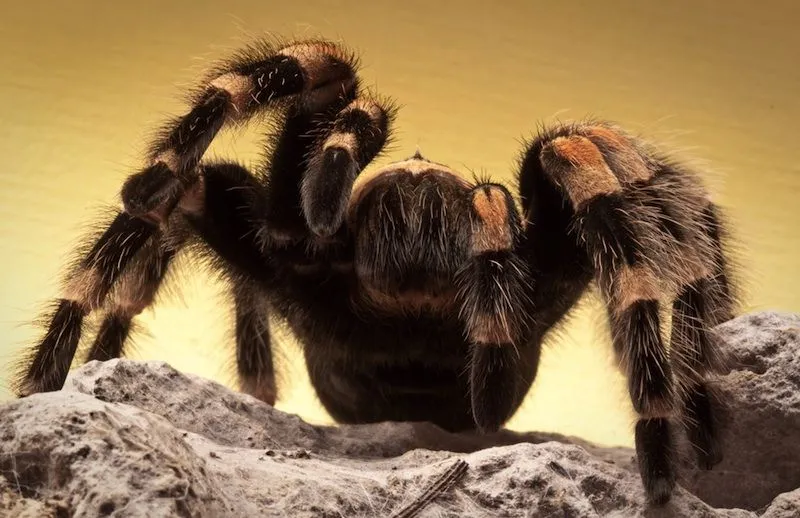
What is a Tarantula Broodfather?
The term “tarantula broodfather” refers to male tarantulas that exhibit parental care behavior, a trait unusual in the spider world. Most male tarantulas, after mating, either die or are driven away by the female. However, in certain species, the male tarantula plays a significant role in protecting the eggs and young spiderlings. These broodbathers are a fascinating subject of study, shedding light on the evolutionary aspects of parental care in invertebrates. Their existence challenges the typical understanding of tarantula behavior and highlights the diversity within the tarantula family. The level of care varies, but it often involves guarding the eggsack and providing some protection to the newly hatched spiderlings, making them truly exceptional in their dedication.
The Role of a Tarantula Broodfather
The role of a tarantula broodfather is multifaceted, going beyond the simple act of mating. The primary function of the broodfather is to safeguard the eggsack, the silken structure containing the female’s eggs. He often stays close to the eggsack, defending it from potential predators or threats. This protective behavior is crucial, as the eggs are vulnerable to various dangers in their environment. Furthermore, in some species, the male may assist in the initial care of the spiderlings. This might include helping them disperse or even providing some level of protection from the elements. The broodfather’s dedication significantly increases the chances of survival for his offspring, a stark contrast to the typical male tarantula’s role, which ends after mating. This cooperative behavior suggests an evolutionary advantage, ensuring the continuation of the species and demonstrating the complex social dynamics of tarantulas.
Broodfather Behavior during Mating

The mating process of a tarantula broodfather is a crucial precursor to his parental duties. Unlike many spider species, the male doesn’t simply mate and disappear. Instead, the male tarantula carefully approaches the female, often using a variety of courtship rituals to avoid being attacked. These rituals can include drumming, vibrating, and presenting gifts. After mating, the male doesn’t retreat but remains near the female. This unusual behavior is indicative of the broodfather’s commitment to the future eggs. The male then waits for the female to lay her eggs and create the eggsack. The success of this mating and his subsequent behavior determines the well-being of his future offspring. This cooperative effort highlights the exceptional social structure that leads to this unusual form of parental care, making the tarantula broodfather a fascinating subject of study and observation.
The Broodfather’s Parental Care
Parental care by tarantula broodbathers is a remarkable behavior, setting them apart from most other spider species. After the eggsack is created, the male often stays close to it, constantly vigilant against potential dangers. This can mean guarding the eggsack from predators, such as other spiders, insects, or even small vertebrates. The male may also regulate the environment around the eggsack, ensuring optimal conditions for the eggs to develop. Once the spiderlings hatch, the broodfather’s role might extend to guarding them until they are old enough to disperse and fend for themselves. This type of care can significantly improve the spiderlings’ survival rates, allowing the species to thrive. The degree of care varies among species, but the fundamental commitment to protecting the offspring is a shared characteristic of these unique tarantulas.
How Broodfathers Protect Eggsacks
Broodfathers employ various strategies to protect their eggsacks. Primarily, they use their physical presence as a deterrent, remaining close to the eggsack to ward off any potential threats. They may position themselves directly in front of the eggsack, becoming a visual barrier and a constant reminder of the risk involved in approaching. When a threat appears, the broodfather can become aggressive, displaying defensive postures or even attacking intruders. Some species may also use silk to reinforce the eggsack, making it more difficult for predators to penetrate. Their protective instincts are driven by a fundamental instinct to ensure the survival of their offspring, showing a remarkable display of dedication to their progeny. This protective behavior is a testament to the diversity and adaptability within the tarantula family, underscoring the exceptional role of the broodfather in the life cycle of these arachnids.
What Happens After the Spiderlings Hatch?
The responsibilities of a tarantula broodfather do not necessarily end when the spiderlings hatch. In some species, the male continues to provide care for the newly emerged spiderlings. This can include guiding the spiderlings to safer areas, protecting them from predators, or even helping them to find food. The broodfather’s presence during this critical stage of life drastically increases the spiderlings’ chances of survival. The level of care varies, with some males providing more intensive support than others. Eventually, the spiderlings become independent, and they disperse to start their own lives. At this point, the male’s parental duties conclude, and he typically retreats to a solitary existence. The duration of care provided by the broodfather is vital to the overall success of the spiderlings, showcasing the significance of this unique parental behavior in the tarantula world.
Broodfather Tarantula: Conservation
The presence of broodfather tarantulas offers opportunities to learn about tarantula behavior and ecology, as well as the benefits of this unique parental system. These tarantulas often live in specific habitats that must be protected to ensure their survival. Habitat destruction, climate change, and the illegal pet trade can pose significant threats to these creatures. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect these unique tarantula species, ensuring that their complex social behaviors are preserved. These efforts may include habitat preservation, captive breeding programs, and regulations to curb the pet trade. Increased knowledge of these spiders helps to support effective conservation measures, leading to their overall protection and the preservation of their unique contributions to the ecosystem, guaranteeing their long-term survival and allowing researchers to keep learning about their amazing behavior.
