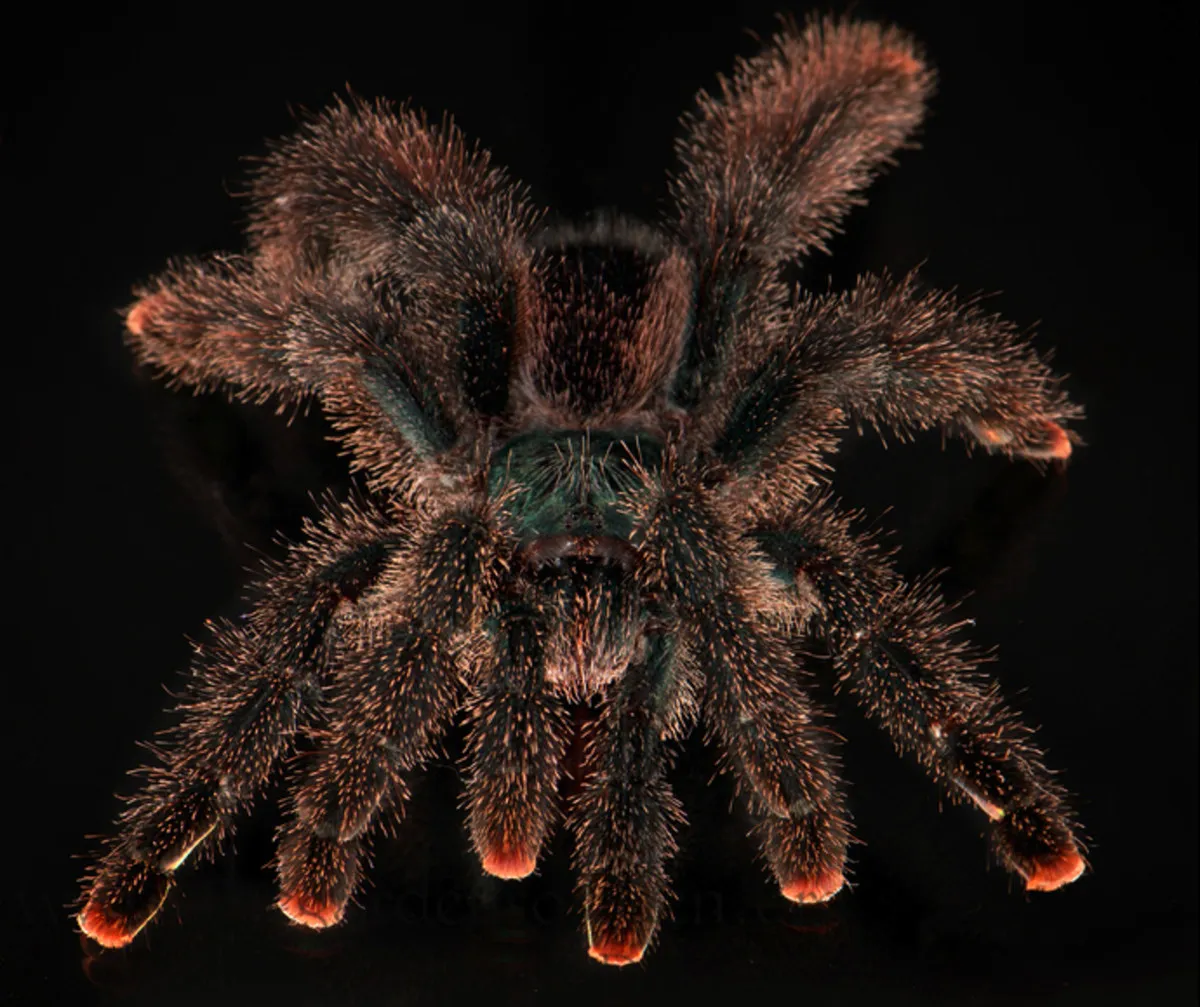
Understanding Tarantula Bites
Encountering a tarantula bite can be a frightening experience. While these spiders are venomous, their bites are rarely life-threatening to humans. However, it’s crucial to understand the potential risks and know how to respond effectively. Tarantulas, though large and intimidating, use their venom primarily to subdue prey. The effects of a bite vary based on the species, the amount of venom injected, and the individual’s sensitivity. This guide will provide essential information to help you navigate a tarantula bite, ensuring you can react calmly and appropriately should the situation arise. Being informed is the first step in mitigating any potential danger and promoting a speedy recovery. It’s important to remember that panic can worsen the physical effects, so understanding the process is vital.
Tarantula Venom and Its Effects
Tarantula venom is complex, containing a mix of enzymes, proteins, and toxins. The primary function of the venom is to immobilize or kill prey. In humans, the effects are typically localized, meaning they are concentrated around the bite site. Common reactions include pain, redness, swelling, and itching. The intensity of these symptoms can differ significantly depending on various factors. Some individuals might experience only mild discomfort, while others may have a more pronounced reaction. Systemic symptoms, affecting the entire body, are rare but can include muscle cramps, nausea, and in very rare instances, difficulty breathing. It’s crucial to monitor the symptoms carefully and seek medical attention if the reaction seems severe or if systemic symptoms develop. The vast majority of tarantula bites will result in symptoms similar to a bee sting.
Common Symptoms of a Tarantula Bite

Recognizing the symptoms of a tarantula bite is essential for proper treatment. The most immediate symptom is usually localized pain at the bite site, often described as a sharp or stinging sensation. This pain can be accompanied by redness and swelling. Itching is another common symptom, which may persist for several hours or even days. In some cases, a blister or small bump might form at the bite site. Other potential symptoms include muscle cramps or spasms, particularly around the area of the bite. These spasms might be more noticeable if the bite occurred on a limb. Less frequently, individuals may experience nausea, dizziness, or headache. If you notice any of these symptoms, or if the localized symptoms worsen significantly, seeking medical advice is recommended. Remember to remain calm and carefully observe any changes in your condition. (Image: tarantula-bite)
The 5 Most Important Things to Know
1. Stay Calm
The immediate reaction to a tarantula bite is often shock and fear. However, staying calm is the most crucial step you can take. Panic can increase your heart rate and blood pressure, potentially worsening the effects of the venom. Take deep breaths and try to remain composed. Find a comfortable position and focus on regulating your breathing. Think clearly, assess the situation, and begin the first aid steps methodically. Remember that tarantula bites are rarely fatal, and the majority of people recover fully. By maintaining a calm demeanor, you can ensure you make rational decisions and assist in your own recovery. (Image: stay-calm)
Why Staying Calm is Crucial

The physiological effects of panic can exacerbate the symptoms of a tarantula bite. Increased heart rate and blood pressure can accelerate the spread of venom throughout the body. Moreover, panic can cloud judgment, making it difficult to assess the situation correctly and take the necessary steps for first aid. Staying calm allows you to focus on identifying the spider (if possible), cleaning the wound, and seeking medical attention if required. It also helps to reduce unnecessary stress on your body, allowing your immune system to work more effectively to neutralize the venom. Remind yourself that most tarantula bites are not life-threatening, and a calm approach significantly improves your chances of a quicker recovery and minimizes potential complications.
2. Identify the Tarantula
If possible and safe, try to identify the tarantula that bit you. This information can be helpful for medical professionals in determining the appropriate treatment. Note the spider’s size, color, and any distinctive markings. A photograph, if you can safely take one, can be invaluable. However, your safety is paramount. Do not risk getting bitten again to identify the spider. If you cannot safely identify the tarantula, don’t worry. Medical professionals can often treat the symptoms without knowing the exact species. Focus on providing accurate details about the bite location, time, and any observed symptoms. The more information you can give, the better equipped the medical staff will be to assess and treat your condition. (Image: tarantula-identification)
Importance of Tarantula Identification
Knowing the species of tarantula can sometimes aid in treatment. While most tarantula bites have similar effects, some species may have slightly different venoms that can cause varying reactions. Medical professionals might use this information to anticipate potential complications or to tailor their treatment plan. Identification can also provide valuable information for future prevention. If you know the species, you can research its behavior and habitat to avoid similar situations in the future. However, in most cases, treatment focuses on managing the symptoms, such as pain and swelling. Even without identifying the tarantula, you can still receive effective care and recover fully. Your description of the bite’s location, the immediate symptoms, and your overall health will be the most important factors for your care.
3. Immediate First Aid
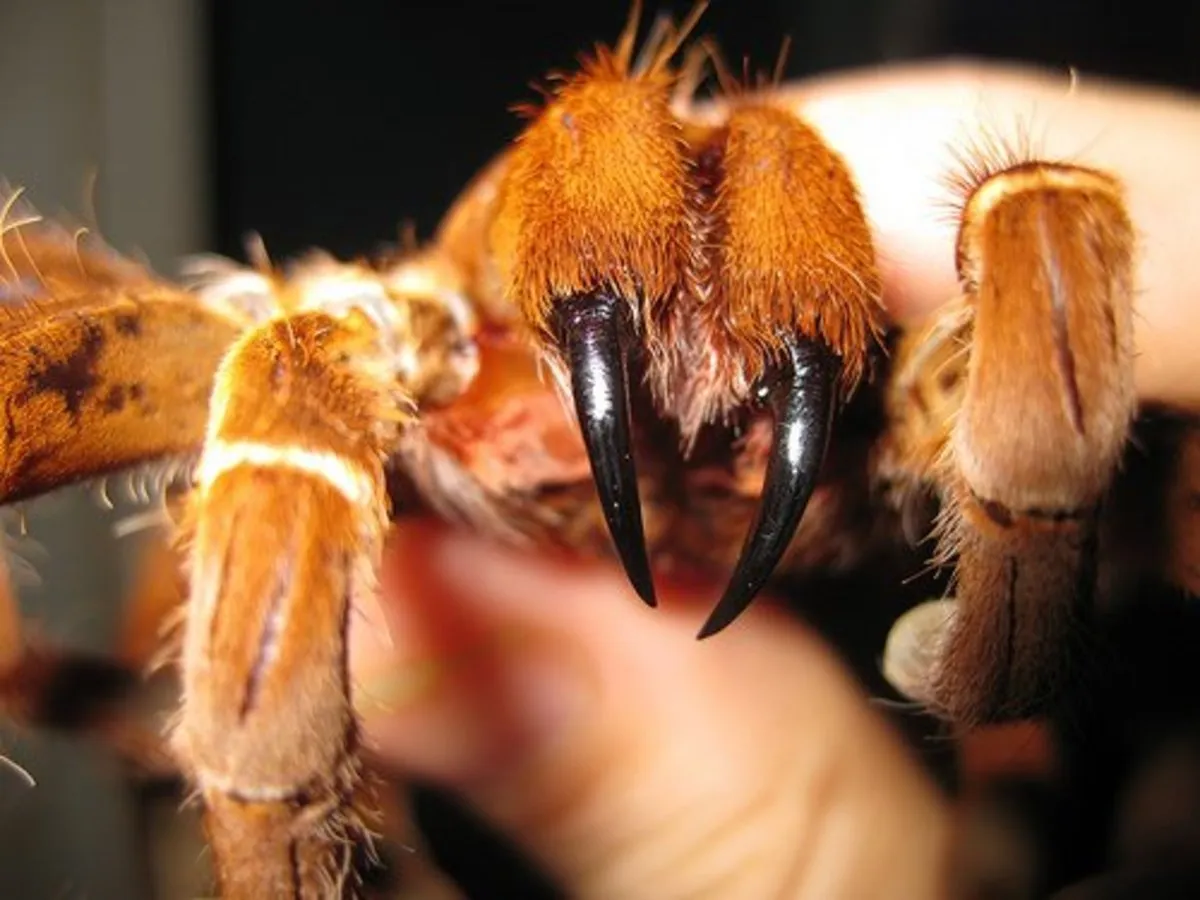

Once you’ve taken steps to stay calm and, if possible, identified the tarantula, start immediate first aid. The first step is to gently clean the bite area with mild soap and water. This will help to prevent secondary infections. Avoid squeezing or attempting to suck out the venom, as this is not an effective method and could cause further tissue damage. If the bite is on a limb, elevate it to help reduce swelling. Apply a cool compress or ice pack to the bite site for 10-minute intervals to help reduce pain and swelling. Monitor your symptoms closely for any worsening. Applying a clean bandage over the bite area will help protect it from further irritation and contamination. Keep the wound clean and dry to promote healing. (Image: cleaning-tarantula-bite)
Cleaning and Wound Care
Proper wound care is essential to prevent infection and promote healing. After cleaning the bite area with soap and water, gently pat it dry. Avoid harsh chemicals or strong antiseptics, as these can irritate the skin. Apply a clean bandage to protect the area from dirt and further trauma. Change the bandage daily, or more frequently if it becomes wet or soiled. Keep the bite site clean and dry. Watch for signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, warmth, or pus. If you notice any of these signs, seek medical attention immediately. Your healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotics or other treatments to address the infection. The goal is to minimize the risk of complications and promote a smooth recovery. Regular wound care is key to a quick healing process.
Pain Management Techniques
Pain management is a crucial part of first aid. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help alleviate discomfort. Follow the dosage instructions carefully. Apply a cool compress or ice pack to the bite site for 10 to 15 minutes at a time, several times a day. This can help reduce pain, swelling, and inflammation. Elevating the bitten limb can also help minimize swelling. Rest and avoid activities that could irritate the bite area. If the pain is severe or does not respond to over-the-counter medications, consult with a doctor. They may prescribe stronger pain relievers or other treatments. Proper pain management ensures you are as comfortable as possible and can facilitate a faster recovery. (Image: pain-management)
4. Seek Medical Attention

While tarantula bites are rarely life-threatening, it’s important to seek medical attention if you experience certain symptoms. Go to a hospital or urgent care facility if you have difficulty breathing, chest pain, severe muscle cramps, or any signs of an allergic reaction, such as swelling of the face or throat. Also, seek medical care if the bite area becomes severely swollen, infected, or if you have persistent, worsening symptoms. It is always best to err on the side of caution. A medical professional can accurately assess your condition and provide appropriate treatment. They may administer pain relief, provide wound care, or prescribe medications to manage any complications. Prompt medical attention can help prevent any serious consequences and ensure a complete recovery. (Image: doctor-tarantula-bite)
When to Consult a Doctor
Consult a doctor immediately if you experience severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing, chest pain, or significant swelling beyond the bite site. Also seek medical attention if you develop a fever, chills, or other signs of infection. If the pain is unbearable or does not respond to over-the-counter pain relievers, a doctor can provide stronger medication. If you notice any unusual symptoms or if your overall health is declining, do not hesitate to consult with a medical professional. Early medical intervention can help prevent complications and speed up your recovery. It is always best to seek expert advice when dealing with a tarantula bite, particularly if you’re concerned about your health.
What to Tell Your Doctor
When you consult a doctor, provide as much detail as possible about the bite. Describe the circumstances of the bite, including where and when it happened. If you saw the spider, provide a description or a photo. Report your symptoms, including the time they started and any changes you’ve noticed. Mention any medications or allergies you have. The more information you give, the better the doctor can assess your condition and provide appropriate treatment. Be open and honest about your concerns and any questions you might have. Your cooperation will help the medical team provide the best care possible and address any potential complications.
5. Prevention and Future Safety
Preventing tarantula bites is crucial, especially if you live in an area where tarantulas are common or if you keep them as pets. Wear protective clothing, such as long sleeves, pants, and gloves, when working in areas where tarantulas might be present. Be cautious when handling objects that might be disturbed, like wood piles, rocks, or debris. If you keep tarantulas as pets, handle them carefully and only when necessary. Always supervise children and educate them about the potential dangers of these spiders. Regular maintenance of your home and yard can help to reduce potential habitats for tarantulas and minimize the risk of accidental bites. Proper precautions will help protect yourself and others from the potential hazards. (Image: preventing-tarantula-bites)
Preventing Tarantula Bites
Several precautions can help prevent tarantula bites. Be vigilant when working or walking in areas where tarantulas are known to live. Avoid putting your hands or feet into places you cannot see, such as under rocks or in dark crevices. Wear protective clothing, especially gloves, when handling firewood, working in the garden, or doing any outdoor activities where tarantulas might be present. Keep your home and yard tidy to minimize hiding places for spiders. If you are keeping tarantulas as pets, use secure enclosures and handle the spiders only when necessary, following the best practices for their care. Education and awareness are key. Teaching children about tarantulas and the importance of avoiding contact can also reduce the risk of bites. By taking these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the chances of a tarantula bite.
Safe Handling Practices
If you keep tarantulas as pets, proper handling is essential for your safety and the well-being of the spider. Always use appropriate tools, such as tongs or a long-handled brush, to move or handle the spider. Never handle a tarantula if you are tired or distracted. Ensure that the enclosure is secure and escape-proof. Regularly inspect the enclosure for any signs of wear or potential escape routes. Always wash your hands thoroughly before and after handling the spider or interacting with its enclosure. Educate yourself about the specific tarantula species you own, including its temperament and potential defensive behaviors. Never put your hands near a tarantula’s fangs. By practicing safe handling techniques, you minimize the risk of bites and create a safer environment for both you and your pet. (Image: safe-handling-tarantulas)
Conclusion

Encountering a tarantula bite can be a stressful experience, but understanding what to do can significantly reduce the potential risks. By staying calm, taking immediate first aid measures, and seeking medical attention when necessary, you can promote a quick and effective recovery. Remember the five key things to know: stay calm, identify the tarantula, apply first aid, seek medical attention when needed, and take precautions to prevent future bites. Knowledge is your best defense against any potential harm. By following these steps, you can navigate this situation with confidence and protect your health. Prioritize your safety and well-being, and remember that most tarantula bites are manageable with the right care and attention.
